MF/HF Stations
Web Page ResourceDescription
MF/HF DSC coast radio stations worldwide with MMSI numbers and frequencies for GMDSS equipment testing. Find testing stations in USA, Europe, Asia, and more for maritime radio.
GMDSS MF/HF Station List + DSC Test Call Frequencies
Coast Radio Stations for MF/HF DSC Testing
When conducting MF/HF DSC tests, you'll need to contact coast radio stations. These stations are organized by region to help you find the most appropriate station for your location.
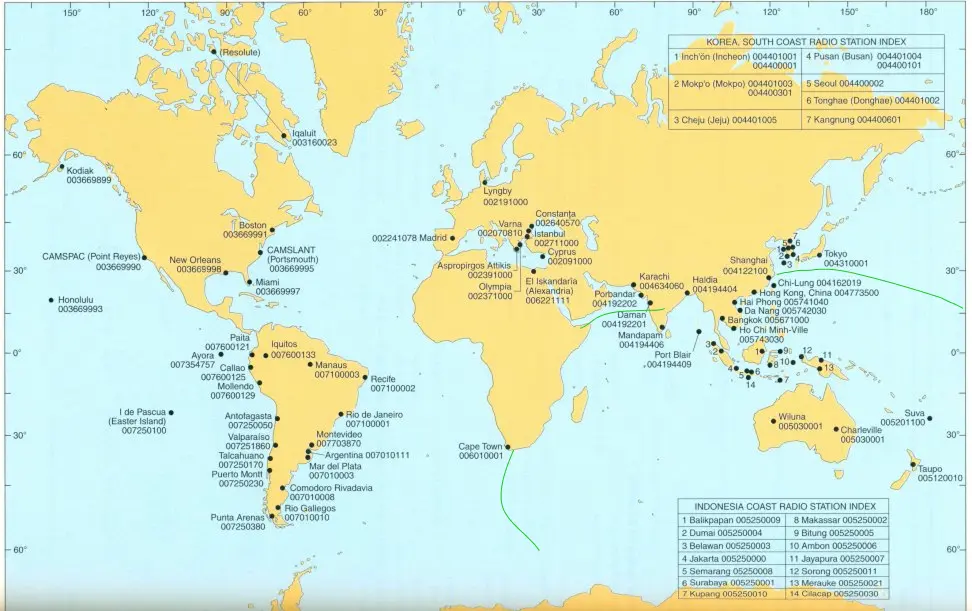
Green line on image shows my experience of successful MF/HF test with Wiluna auto acknowledgment.
Click on any station name or MMSI to copy it to your clipboard.
Station Legend:
| Station | MMSI | Frequency | Coverage Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boston | 003669991 | 8MHz | East coast USA |
| New Orleans | 003669998 | Caribbean Sea | |
| Point Reyes/CAMSPAC | 003669990 | 4MHz | West coast USA |
| Honolulu | 003699993 | Pacific | |
| Miami | 003669997 | USA | |
| Kodiak | 003669899 | Alaska |
| Station | MMSI | Frequency | Coverage Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cape Town | 006010001 | Cape of Good Hope approaches | |
| Lyngby | 002191000 | 2MHz | North/Baltic Seas |
| Madrid | 002241078 | 8MHz | Mediterranean Sea |
| Istanbul Radio | 002711000 | 16MHz/12MHz | Black Sea |
| Olympia Radio | 002371000 | Any frequency | Mediterranean Sea |
| Station | MMSI | Frequency | Coverage Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shanghai | 004122100 | Any frequency | East China Sea & Coastal China |
| Hong Kong | 004773500 | 8MHz | South China Sea - Pearl River Delta |
| Ho Chi Minh-Ville | 005743030 | 16MHz/12MHz | Vietnam |
| Bangkok | 005671000 | 8MHz | Thailand |
| Dalian | 004121300 | 2/4MHz | China |
| Hai Phong | 005741040 | Vietnam | |
| SEOUL | 004400002 | Korea | |
| Wiluna | 005030001 | Auto-acknowledge | Australia/Indian Ocean |
| Busan Coast Radio | 004401004 | 12MHz | Korea Strait & Sea of Japan |
| Incheon Coast Radio | 004401001 | 8MHz | Yellow Sea - Korea West Coast |
| Ambon Radio | 005250006 | 8MHz | Eastern Indonesia/Banda Sea |
| Balikpapan Radio | 005250009 | 8MHz | Central Indonesia - Makassar Strait/Java Sea |
| Mumbai Radio | 004192203 | 12MHz | Arabian Sea - NW Indian Ocean |
| Chennai Radio | 004194401 | 12MHz | Bay of Bengal - NE Indian Ocean |
| Tokyo Coast Guard Radio | 004310001 | 12MHz | NW Pacific & Japanese waters |
| Station | MMSI | Frequency | Coverage Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jeddah Radio | 004030000 | 12MHz | Red Sea - East side |
| Bandar Abbas Radio | 004225300 | 8MHz | Persian Gulf |
| Alexandria Radio | 006221111 | 8MHz | Eastern Mediterranean & Approaches to Suez |
| Mauritius Radio | 006452700 | 12MHz | Southwestern Indian Ocean |
| Station | MMSI | Frequency | Coverage Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rio de Janeiro Radio | 007100001 | 12MHz | Southwest Atlantic - Brazilian coast |
| Buenos Aires Radio | 007010111 | 8MHz | Southwest Atlantic - Río de la Plata |
| Montevideo Radio | 007703870 | 8MHz | South Atlantic - River Plate area |
DSC Test Call Frequencies
Digital Selective Calling (DSC) is a critical component of the GMDSS system. To ensure your equipment functions properly, regular testing is required on approved frequencies.
4207.5 kHz (auto-acknowledgment from all USCG stations except Guam)
6312 kHz
8414.5 kHz
12577 kHz
16804.5 kHz
Required GMDSS Equipment Tests
To maintain safety at sea, GMDSS equipment must be regularly tested according to a specific schedule. Each test ensures that critical communications systems will function properly in an emergency.
DAILY TESTS
Daily tests are essential to verify the basic functionality of your GMDSS equipment. These quick checks help identify issues before they become critical.
VHF DSC
Verify internal connections
Check transmitting power output
Examine display functionality
Test DSC system using built-in test function (no signal transmission)
MF/HF DSC
Perform internal test using built-in facility without transmitting signals
INMARSAT-C
Verify proper login status to appropriate Ocean Region
Check status information displayed on screen header
Backup Power
Examine reserve battery charge status
Record results in radio log
Other Daily Checks
Verify paper availability in MF/HF, Navtex, and INMARSAT-C printers
WEEKLY TESTS
Weekly tests ensure that your GMDSS equipment can communicate properly with external stations. These tests verify both transmission and reception capabilities.
MF/HF DSC
Don't forget to perform test by manually switching off main supply (where applicable) switch to test battery transmit, receive
Conduct DSC test call on any HF channel (MMSI numbers for stations can be found in the tables above)
Options if auto-acknowledgment isn't available:
Contact station via R/T requesting acknowledgment
Send test call to nearby vessel with confirmation request
MF/HF Wave Propagation
Time of Day Effects: MF/HF radio waves propagate differently depending on the time of day. At night, these frequencies typically travel farther due to changes in the ionosphere.
Night Advantage: During nighttime, the D-layer of the ionosphere (which absorbs radio waves during daylight) disappears, allowing signals to bounce off higher ionospheric layers and travel much greater distances.
Testing Tip: If you're having difficulty reaching distant stations, try conducting tests after sunset or before sunrise when propagation conditions are often more favorable, especially for MF frequencies (2 MHz band).
Important Note: If the vessel did not receive a response from a coast station, it may document a test vessel-to-vessel communication in the log. However, at the first opportunity, a proper coast station call should be performed to ensure full compliance.
Do not forget to press the RTT (Radio Telephone Transmit) voice button momentarily during testing to verify output functionality. In some cases, DSC may successfully send and receive acknowledgments from stations while the voice output circuit operates separately, requiring individual verification. I have experienced this issue on two different vessels. Be cautious when testing on 8 MHz frequencies, as I have experienced total power loss when hitting the RTT button on these frequencies.
VHF DSC
Conduct internal test between ship's two VHF sets
Use selective calling between duplicate sets (preferably at low power)
Ensure automatic acknowledgment feature is active
No live VHF DSC test required
VHF units usually have built-in daily test functions to cover all test requirements specified by the manufacturer
MONTHLY TESTS
Monthly tests are more comprehensive and focus on emergency equipment that must function reliably in a crisis situation.
INMARSAT-C Monthly Test
Run built-in diagnostic test according to manufacturer's instructions
Use the Performance Verification (PV) built-in tool to verify system functionality
Perform distress button test (follow specific protocol in manual)
Don't forget to test SSAS (Ship Security Alert System) - refer to your SMS or consult Ship Security Officer
Verify proper data transmission and message reception
Check printer functionality by printing test message
Verify all EGC (Enhanced Group Call) functions are operational
Always refer to the specific manufacturer instructions for in-depth test procedures
Handheld VHF
Test on frequency other than Ch.16 (156.8 MHz)
Skip if sealed unit makes testing impractical
Check battery expiration dates
Verify all required stations are properly loaded
Recheck batteries status and station after each drill
406 MHz EPIRB
Run self-test function (usually by switching to test mode without breaking the seal, observing light signals as confirmation of success)
Check for test procedure instructions on EPIRB body or in the manual
Inspect for physical damage
Check battery expiration date
Verify HRU (hydrostatic release unit) condition
Ensure lanyard and water contacts are intact
Confirm safety clip is properly secured
Check manufacturer's instructions for specific testing procedures
AIS-SART
Visual inspection
Check battery expiration date
Verify legible MMSI label
Confirm support stand integrity
When testing in port, notify authorities beforehand
Verify test success via ship's AIS equipment (AIS unit, ECDIS, radars)
X-band SART
Visual examination
Check battery expiration date and safety clip position
Avoid sea-based testing
Notify port authorities for port-based testing
For necessary sea-based tests:
Check 3-cm radar for nearby vessels
Make safety priority VHF DSC announcement
Limit SART activation to 2-3 radar sweeps
Check manufacturer's instructions for specific testing procedures. Usually done by activating the test button on the unit for a few seconds at some distance from the radar, e.g., ship's bridge wing
GMDSS Batteries
Thoroughly examine emergency batteries
For non-sealed wet cells: inspect each cell individually
For other battery types: visual examination
Document results in GMDSS Radio Log
Replace as needed per manufacturer recommendations
Check manufacturer's instructions for specific testing procedures. On modern vessels, batteries are sealed and cannot be tested directly, so they should be checked for signs of damage and proper functionality
ANNUAL INSPECTIONS
Annual inspections provide a comprehensive evaluation of your entire GMDSS system.
Performed by qualified radio surveyors
Comprehensive equipment testing using professional GMDSS testers
Equipment Manuals: Always refer to manufacturer instructions and equipment manuals for in-depth testing details specific to your model. If you have specialized knowledge about specific equipment, consider contributing to our Maritime Resource Hub to help fellow seafarers.
Important Reminders
1. Always maintain proper documentation of all tests in your GMDSS Radio Log.
2. Never conduct tests that might cause false distress alerts.
3. When in doubt about procedures, consult the equipment manuals or contact the manufacturer.
GMDSS Logs and Responsibilities
GMDSS Log Requirements:
- Every GMDSS log entry must include vessel position (latitude/longitude)
- Both local time and UTC time must be recorded with each entry
- All tests, failures, repairs, and incidents must be documented
Onboard Responsibilities:
- Typically, the 2nd Officer serves as primary GMDSS tester
- 3rd Officer often serves as emergency response person. If you have another SMS system please visit lagom poll's click to share what is best system.
- All Officers of the Watch (including the Captain) are responsible for correctly filling GMDSS logs
Despite technological advances, many vessels still rely on paper-based GMDSS logs. A standardized electronic logging system would improve consistency and reduce administrative burden. If you know of effective electronic systems, please share at our Maritime Resource Hub.